Types of ABA Data Collection Methods
Applied behavior analysis (ABA) is driven by data collection. Every decision made in ABA therapy—from designing behavior interventions to modifying treatment plans—is backed by behavioral data collection. Selecting the right ABA data collection methods is essential for tracking a learner’s progress, ensuring compliance, and optimizing outcomes across your practice.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the most common data collection methods, explain how they’re applied in real-world settings, and show you how AI-powered ABA data collection systems, like Raven Health’s all-in-one practice management platform, can streamline your entire data collection process, while maintaining data security.
What Is Data Collection in ABA?
In applied behavior analysis, data collection refers to the systematic process of recording behavioral and environmental variables to evaluate progress, inform decision-making, and ensure consistent treatment outcomes via analysis tools.
By tracking what happens before, during, and after a learner’s behavior occurs, behavior analysts can use ABA data collection when it comes to:
- Evaluating intervention effectiveness with precise data collection tools
- Assessing behavior change over time using measurable indicators
- Monitoring target behavior trends with consistent data collection methods
- Adjusting skill acquisition programs based on real-time data collection
- Identifying behavior patterns that inform proactive decision-making
- Guiding task analysis and functional behavior assessments (FBAs) with structured observation
- Meeting ABA compliance standards through reliable, high-quality data collection
Whether you’re using continuous data collection methods or discontinuous data collection methods, the data collected must be valid, reliable, and consistent to meet ABA standards.
Why Is Data Collection Important in ABA?
Effective ABA data collection is not just about documentation—it’s about delivering meaningful clinical care. Reliable data collection techniques allow you to:
- Track progress over time with comprehensive ABA data collection
- Make data-driven decisions grounded in high-quality data collection
- Adjust interventions based on real-time data collection insights
- Reduce human error through digital data collection systems
- Ensure that data collectors consistently apply each data collection method
- Use advanced data collection tools that align with best practices in ABA therapy

Categories of ABA Data Collection Methods
There are several different data collection methods used in applied behavior analysis, and each has its own purpose depending on the learner’s needs, the environment, and available resources. These methods fall into two primary categories: continuous data collection methods and discontinuous data collection methods.
Continuous Data Collection Methods
These data collection methods involve recording each time a behavior occurs. Common continuous ABA data collection methods include:
- Frequency recording (how often the behavior occurs using direct data collection)
- Rate data collection (frequency over time)
- Duration recording (how long a specific behavior lasts based on session duration data collection)
- Latency recording (time from prompt to behavior start captured via accurate latency data collection)
- Inter-response time (IRT) (time between two behaviors using interval-based data collection)
Continuous methods provide accurate data, but they require focused attention from data collectors and are ideal for high-priority target behaviors.
Discontinuous Data Collection Methods
Discontinuous data collection methods track whether or not a behavior occurs during specific intervals. These ABA data collection methods include:
- Whole interval recording
- Partial interval recording
- Momentary time sampling
These measurement systems are useful when recording data continuously isn’t feasible, such as in group settings or classrooms. These discontinuous data collection techniques offer efficient alternatives while still producing meaningful insights.
Most Common ABA Data Collection Methods
Let’s break down the most widely used ABA data collection methods in the field:
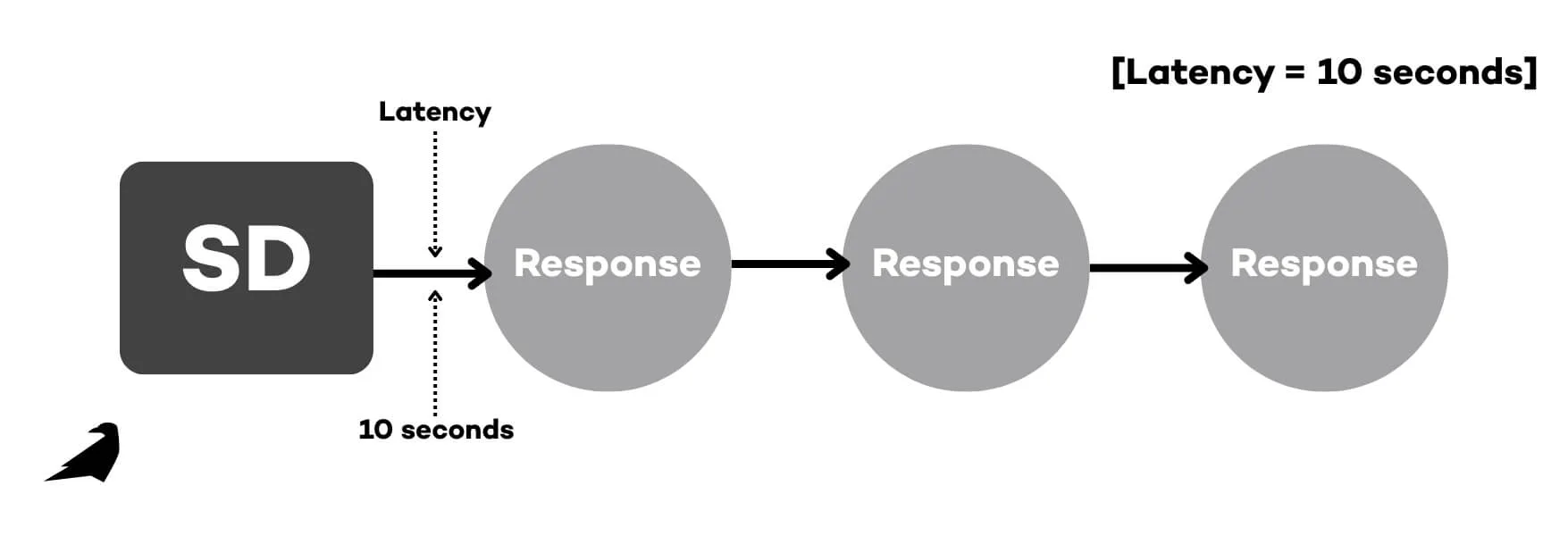
1. Latency Recording
The latency recording method involves counting the time between a cue or discriminative stimuli (SD) and when the behavior occurs. For example, if a therapist gives a direction and the learner responds after 10 seconds, that’s your latency data. Useful for analyzing responsiveness and evaluating skill acquisition delays.
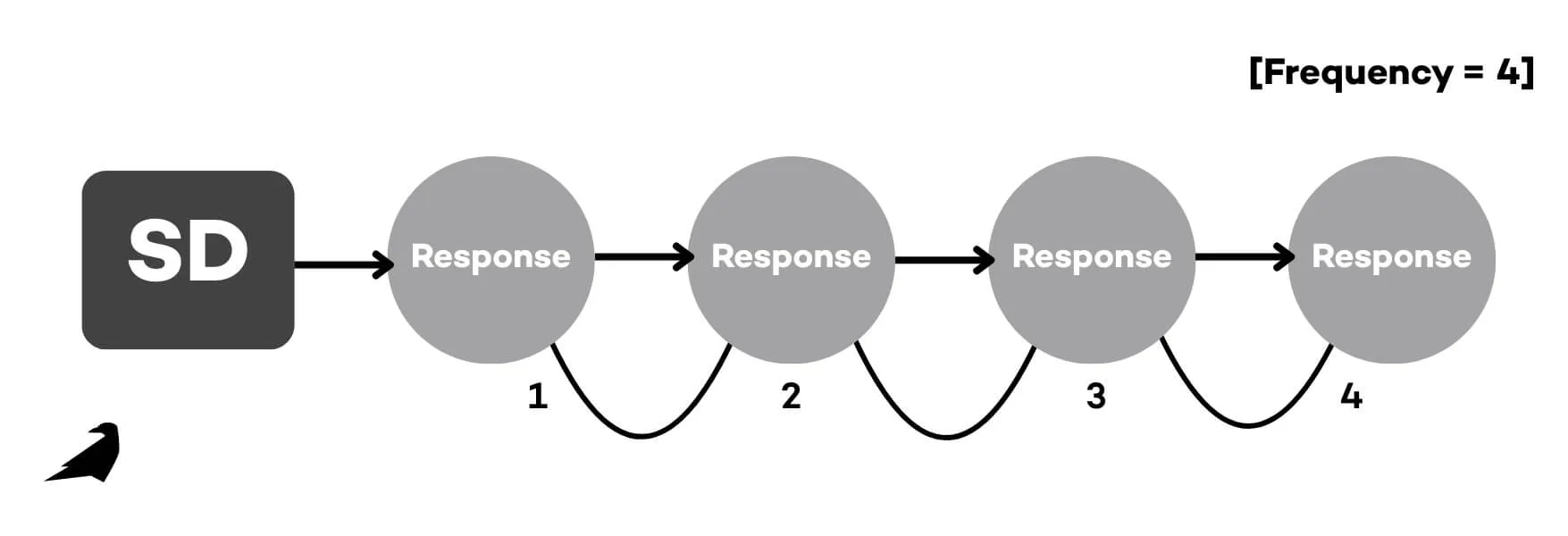
2. Event Recording (Frequency and Rate)
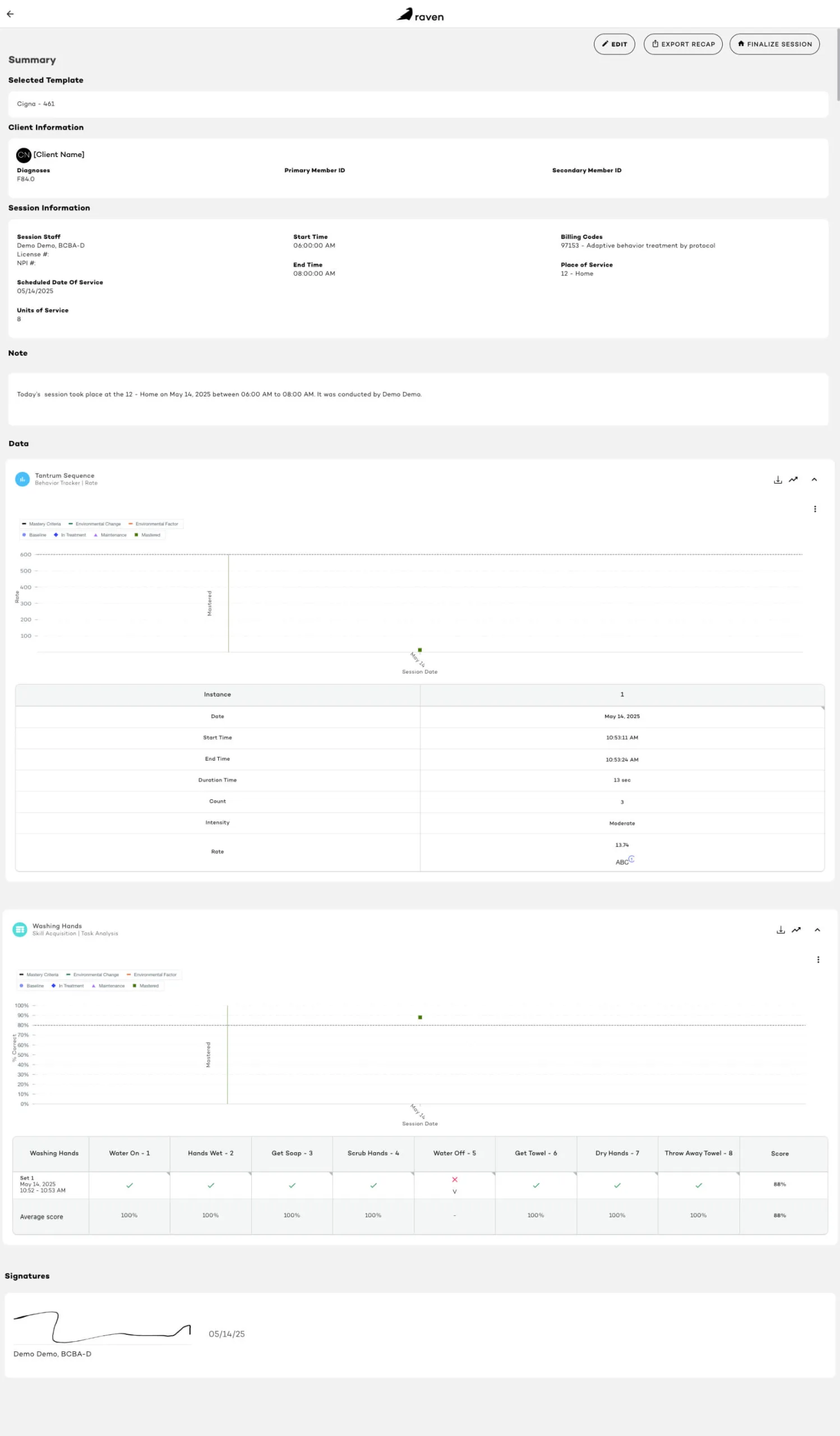
Event recording tracks how many times a specific behavior occurs. For instance, a learner raises their hand 4 times in a session. When paired with session length, this continuous method helps determine frequency over time. It’s a go-to when the target behavior is clear and observable.
3. Duration Recording
The duration recording method measures how long a behavior occurs, like tracking the total time a learner spends off-task. Duration data provides insight into sustained behaviors and supports precise data collection needs.
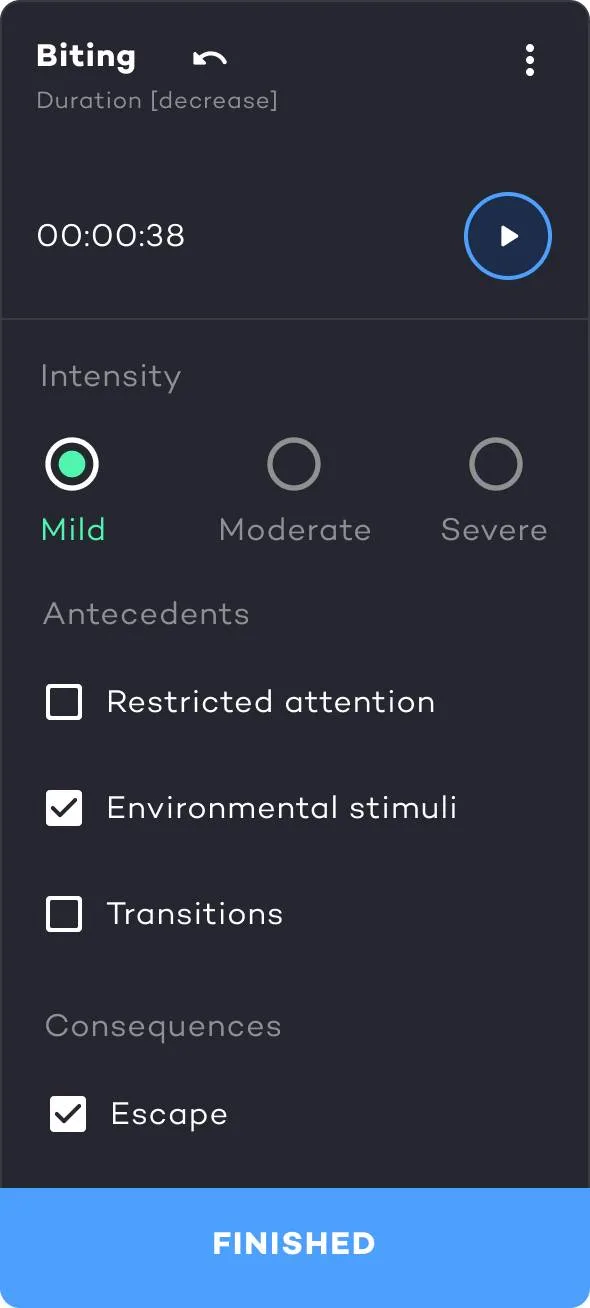
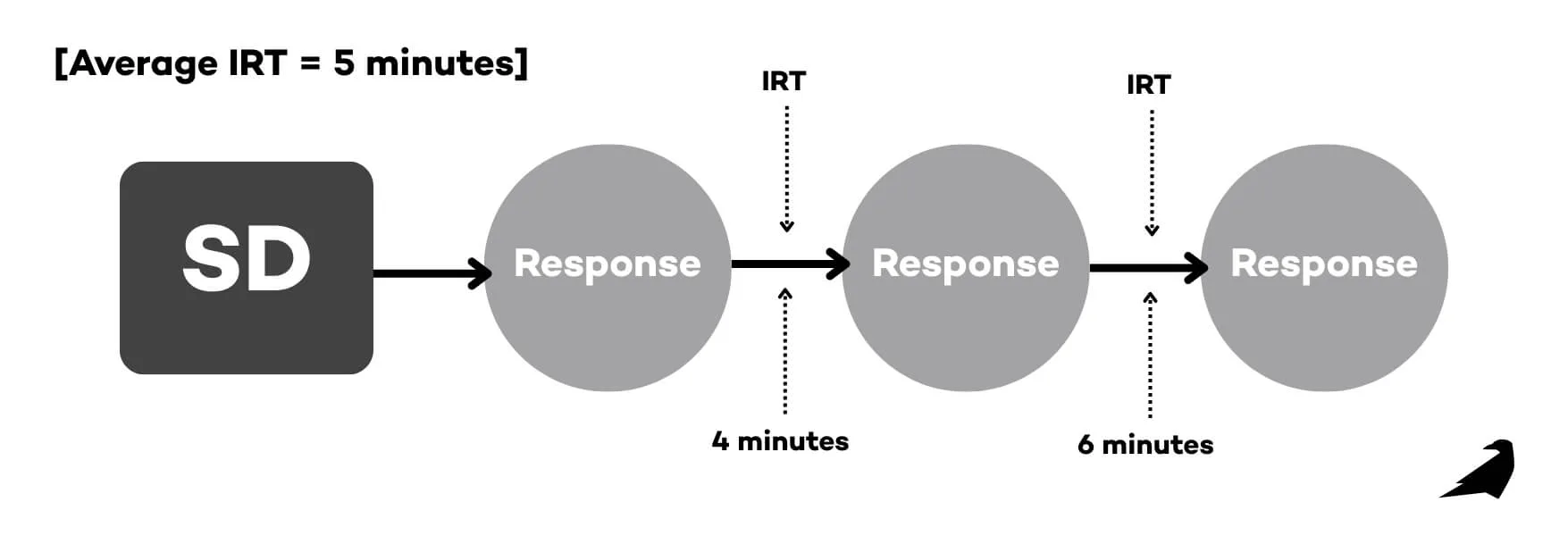
4. Inter-Response Time (IRT)
IRT measures the time between responses. For example, if a learner engages in stereotypy every 5 minutes, the data can help identify patterns. This is a strong choice for low-rate behaviors when you need to closely track progress.
5. Whole Interval Recording
A whole interval recording method marks a behavior only if it occurred during the entire interval. This type of interval data may underestimate frequency, making it ideal for increasing desired behaviors. It promotes a consistent whole interval recording, along with a structured observation of a learner’s behavior.

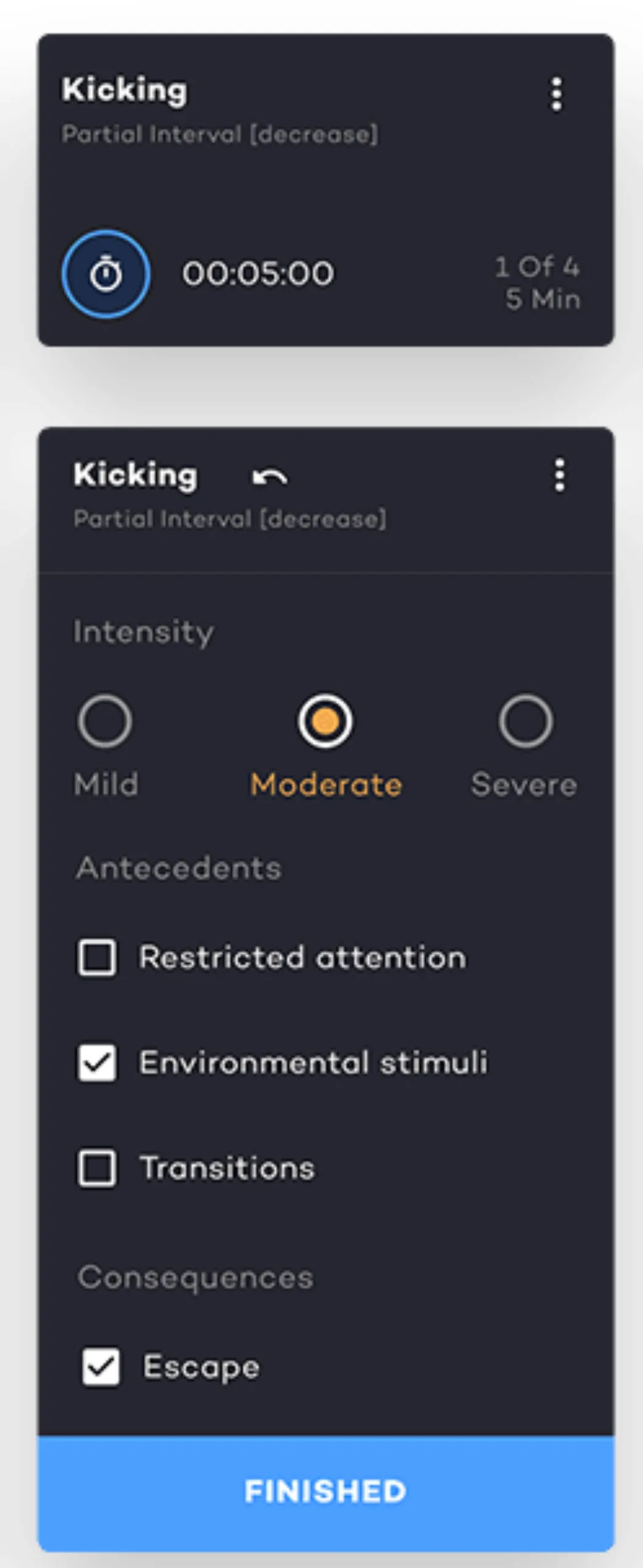
6. Partial Interval Recording
Partial interval recording logs if the target behavior occurred at any point during the interval. This type of interval data often overestimates behavior frequency—helpful when aiming to decrease high-rate behavior occurrences. As a widely used form, partial interval recording efficiently captures brief behaviors.
7. Momentary Time Sampling
Momentary time sampling, also shortened as ‘time sampling’ is a method that checks if a target behavior occurs at the end of each interval. It’s efficient and minimally disruptive, often used in classrooms. As another type of interval recording, it helps behavior analysts collect data during instruction.
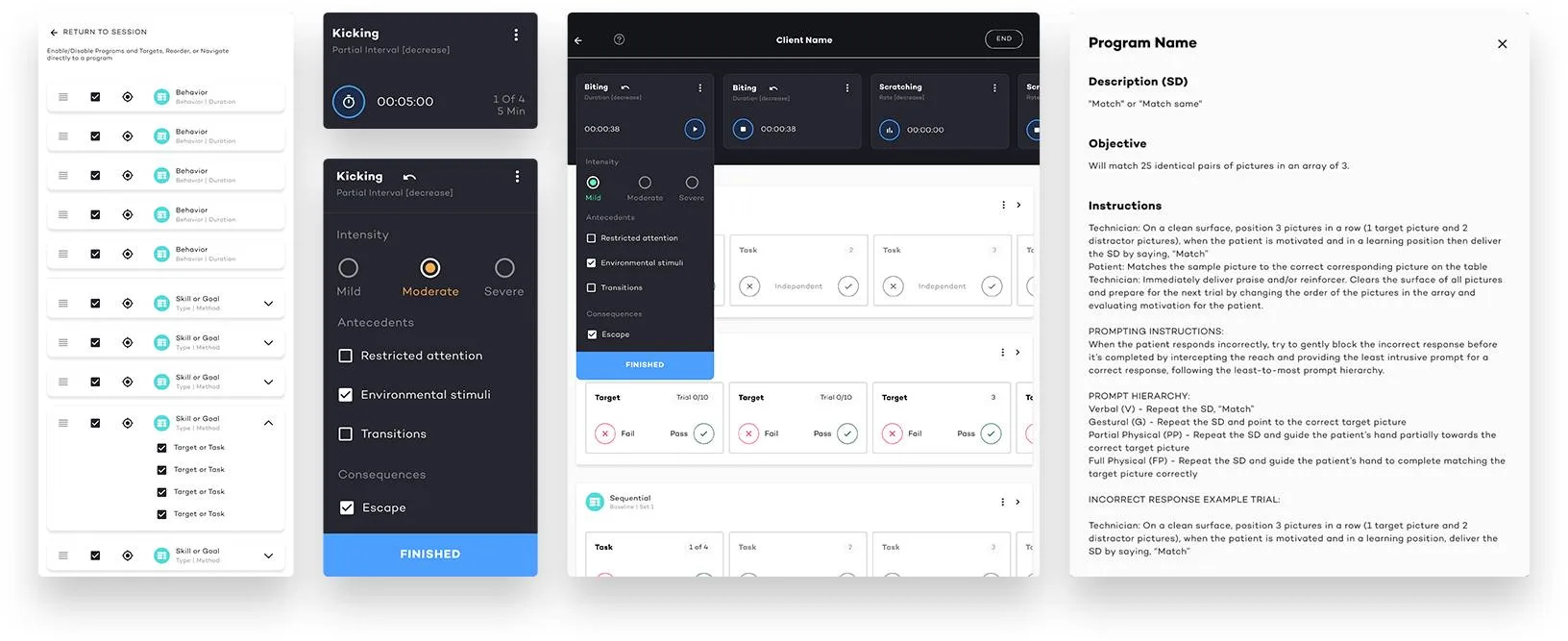
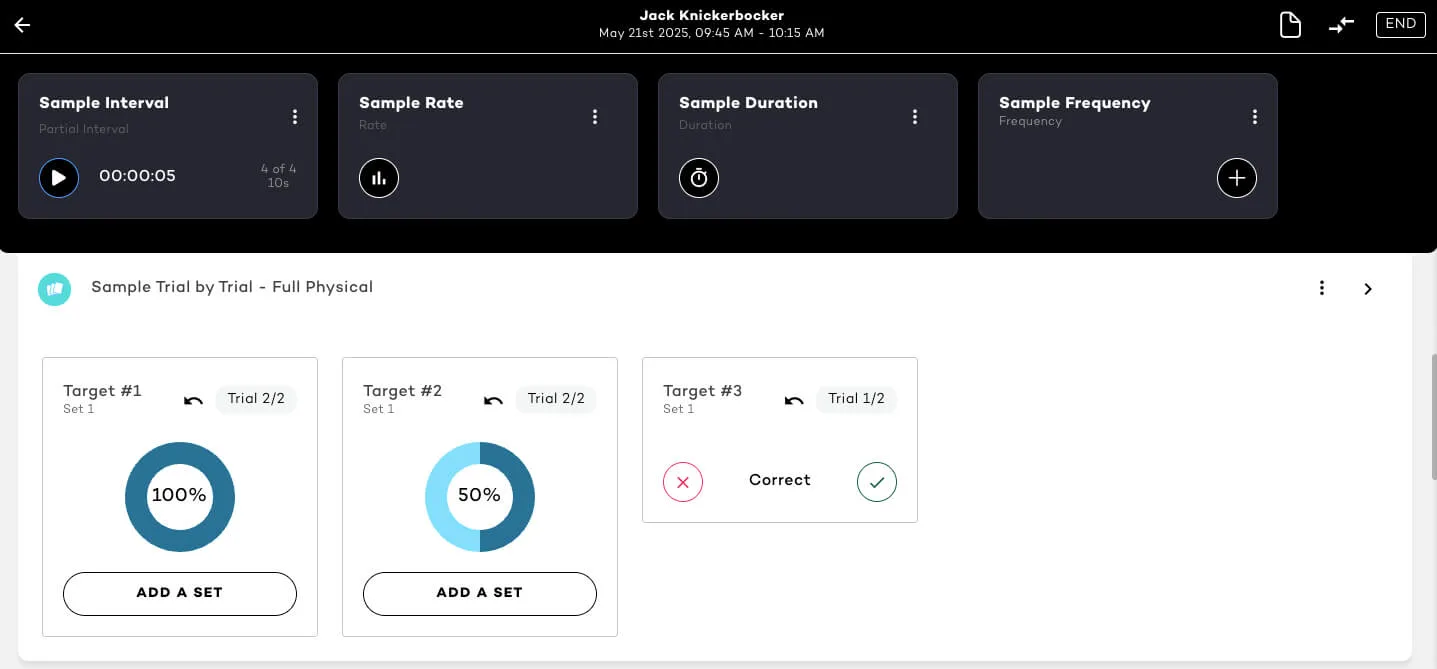
8. Trial-by-Trial / Per Opportunity Recording
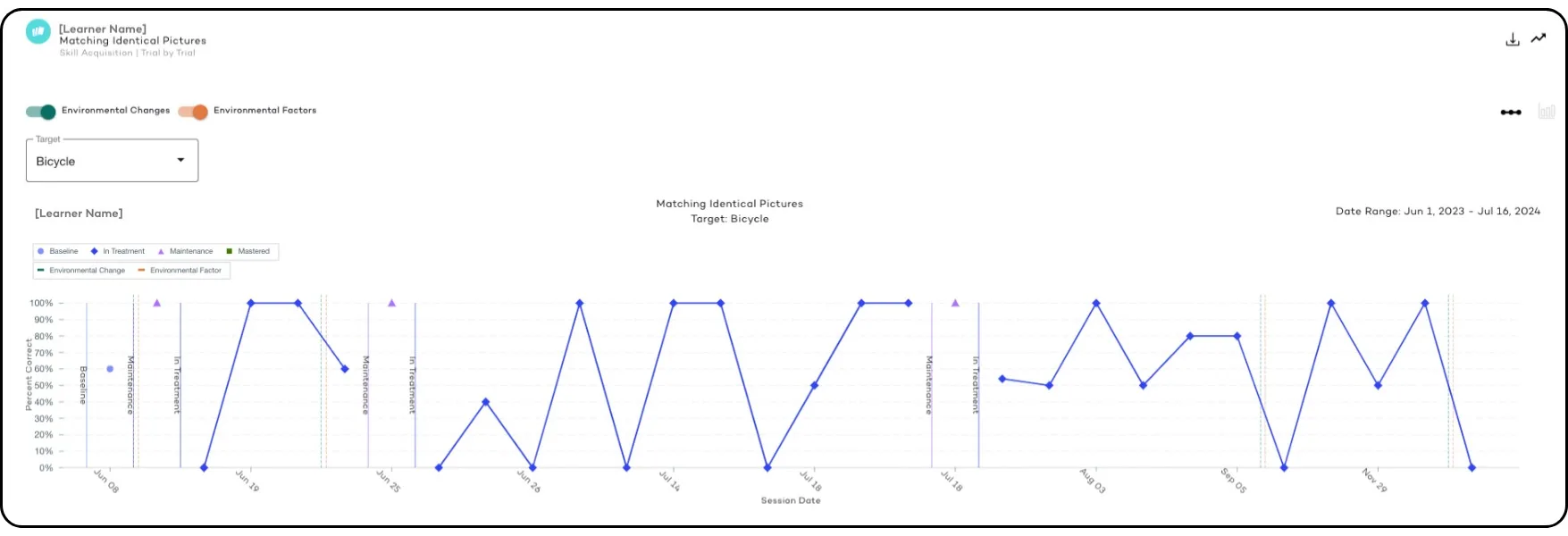
Used primarily in discrete trial training (DTT), this method logs responses per teaching opportunity. It’s highly effective for skill-building, task analysis, and analyzing data across structured sessions—especially for tracking changes in a learner’s behavior over time. By breaking complex skills into smaller steps, task analysis ensures accurate measurement of progress and mastery in the data collected.
9. Rating Scales
Rating scales offer a subjective yet valuable perspective. For instance, aggression might be rated from 1–5, or even 0%-100%. While not as objective, they complement other methods and are particularly useful in behavioral health settings.
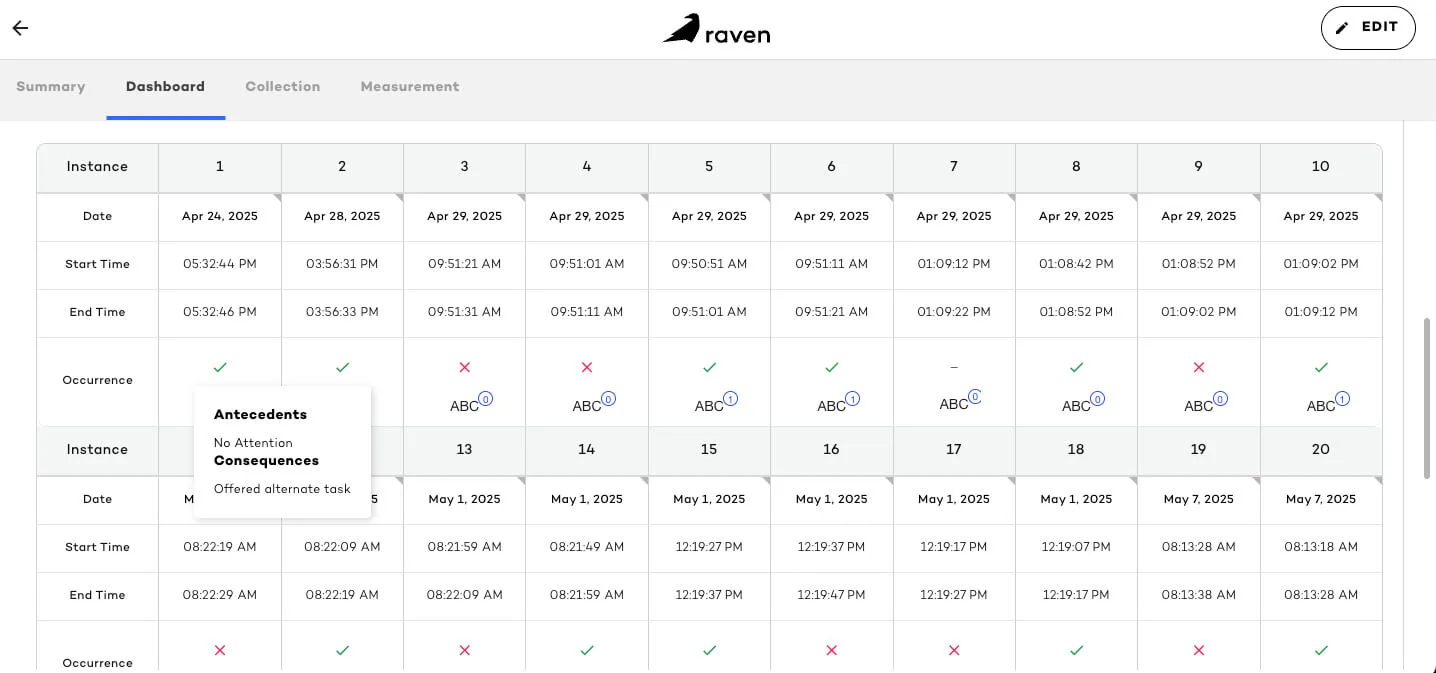
10. Antecedent-Behavior-Consequence (ABC) Data
ABC data involves logging what occurred before (antecedent), during (behavior), and after (consequence) an incident. An example of ABC data is as follows:
- Antecedent: Asked to complete a chore
- Behavior: Screaming
- Consequence: Avoided the task
The antecedent behavior consequence model is essential in behavioral health for identifying the function of a target behavior and developing behavior intervention plans via the data collected. Research studies show that accurate ABC data enables analysts to better track progress and develop support strategies within ABA therapy.
11.Scatterplot Analysis
Scatterplots help identify patterns in a learner’s behavior across days or times. Particularly helpful when a behavior occurrence appears random, this method is a staple in long-term planning and behavioral health strategy.
These methods are grounded in research-based principles outlined in Cooper, Heron, & Heward’s Applied Behavior Analysis (2019), a foundational text in the field.
Choosing the Right Data Collection Method
Selecting the appropriate ABA data collection method depends on various factors:
- Whether you’re targeting behavior reduction or skill acquisition
- Whether the behavior occurs continuously or occasionally
- Availability of staff and time for recording data
- Which data collection methods give you the most accurate data
- Whether data collection software can support the process
- How well the method fits within ABA compliance guidelines
To put things simply, choosing the right method depends on the target behavior, context, and purpose of the intervention. By training data collectors to consistently use the chosen data collection method, ABA professionals ensure reliable insights. In some cases, combining your primary method with other data collection methods can offer a more comprehensive view, especially when conducting functional behavior analysis or planning interventions.
Regardless of the approach, the goal remains the same: to collect data effectively and drive better outcomes through intentional, informed decision-making. The key is to use ABA data collection methods that balance reliability, efficiency, and clinical utility.

The Role of ABA Data Collection Software
Modern data collection systems are transforming how ABA therapy practices manage the data collection process. Gone are the days of clipboards and manual spreadsheets. Today’s ABA data collection software empowers Board Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAs) and Registered Behavior Technicians (RBTs) to:
- Collect data in real-time with mobile-friendly data collection tools
- Customize data sheets for different ABA data collection methods
- Conduct real-time data analysis to identify patterns
- Improve data security and HIPAA compliance using secure data collection platforms
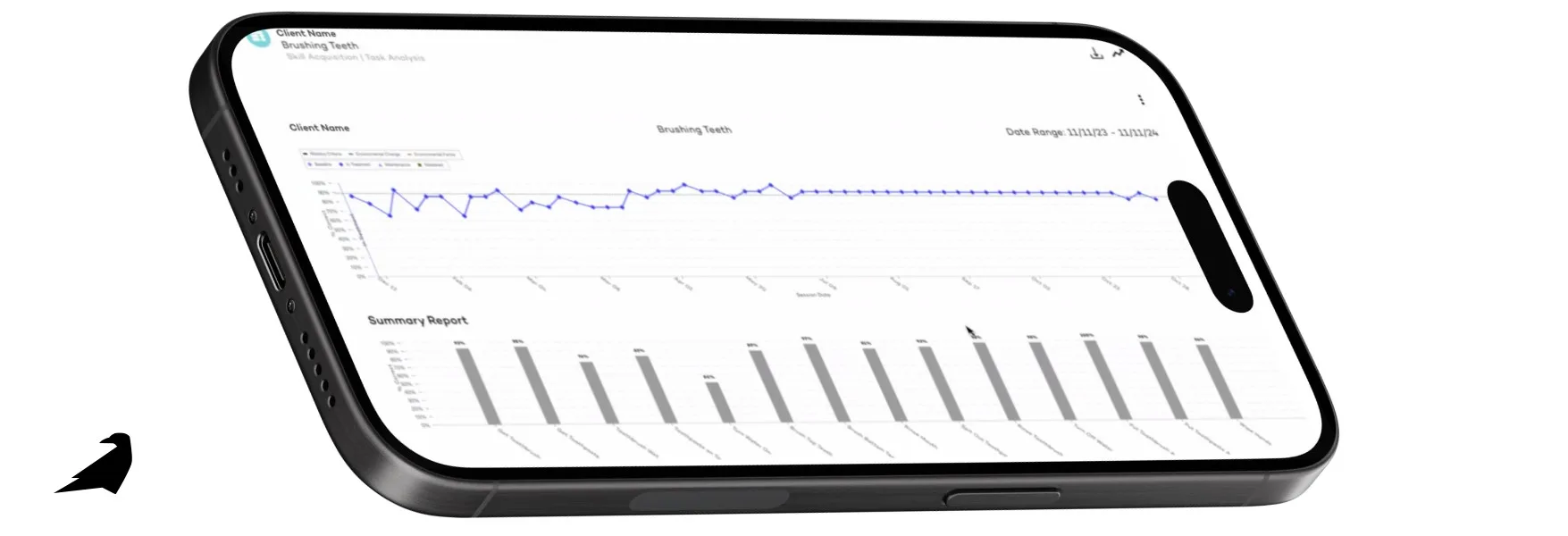
How Raven Health Simplifies ABA Data Collection
At Raven Health, we’ve designed an all-in-one, AI-powered practice management platform that simplifies ABA data collection from start to finish, while maintaining data security. Our electronic data collection systems support every method discussed above—whether you’re tracking ABC data, conducting duration recording, or implementing trial-by-trial data sheets.
With Raven Health, ABA providers can:
- Analyze target behaviors through streamlined skill acquisition data tracking
- Automate data collection workflows with intelligent tools
- Reduce burnout by easing data collection for RBTs and BCBAs
- Ensure accurate data collection through smart prompts
- Eliminate paper data sheets to improve efficiency and reduce manual errors
- Align data collection techniques with best-practice behavior analysis
- Stay ahead of the curve with AI-driven analysis tools for long-term data collection success
Whether you’re about to start an ABA company or you’re scaling your existing operation, Raven Health offers different data collection methods that are built for modern care.
Ready to Improve Your Data Collection Process?
If you’re serious about improving outcomes and operational efficiency, it’s time to re-envision how your team handles ABA data collection. Let Raven Health help you modernize your workflows, enhance data security by minimizing errors, and deliver better care with smart ABA data collection software.
Schedule a demo today to discover how Raven Health’s AI-powered data collection software has elevated countless ABA therapy practices.
If you’re ready to jump right in, experience 30 risk-free days of our ABA data collection software with a hands-on trial.
References: Cooper, J. O., Heron, T. E., & Heward, W. L. (2019). Applied Behavior Analysis (3rd ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Pearson.